PROTACs are very promising molecules in drug discovery. Although PROTACs have been shown to be highly efficient against a variety of targets, most degraders reported to date show limited intrinsic tissue selectivity. Inspired by ADCs, PROTAC-antibody conjugates have been developed as an alternative method for selective delivery of broad-spectrum PROTACs to specific cell types, thereby minimizing undesired side effects.
As a leading service provider in drug discovery and research, BOC Sciences is fully capable and committed to providing one-stop PROTAC discovery services. We provide comprehensive services for PROTAC-antibody conjugates. Our advanced PROTAC platform meets the new drug development needs of our customers around the world.
Introduction
Proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTACs) are heterobifunctional molecules that are capable of degrading target proteins in cells and offer the potential for improving biological activity relative to traditional small molecule inhibitors. PROTAC consists of three parts: an E3 ubiquitin ligand and a target protein ligand, as well as a linker specially designed to link the two together. However, these degraders are often shown poor tissue selectivity and low bioavailability.
Based on the continuous clinical success of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), in order to enable more efficient delivery of PROTAC in vivo, several studies have explored coupling PROTAC with monoclonal antibodies. Degrader-antibody conjugates (DACs) are novel entities that combine a PROTAC payload (degrader) with a monoclonal antibody via some type of chemical linker, which have several potential advantages over PROTAC molecules:
- target PROTAC molecules to specific tumors or tissues;
- can deliver the degraders with poor physicochemical or DMPK (drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics) properties in vivo;
- avoid complex formulations that are often necessary for PROTACs to gain activity upon in vivo exposure.
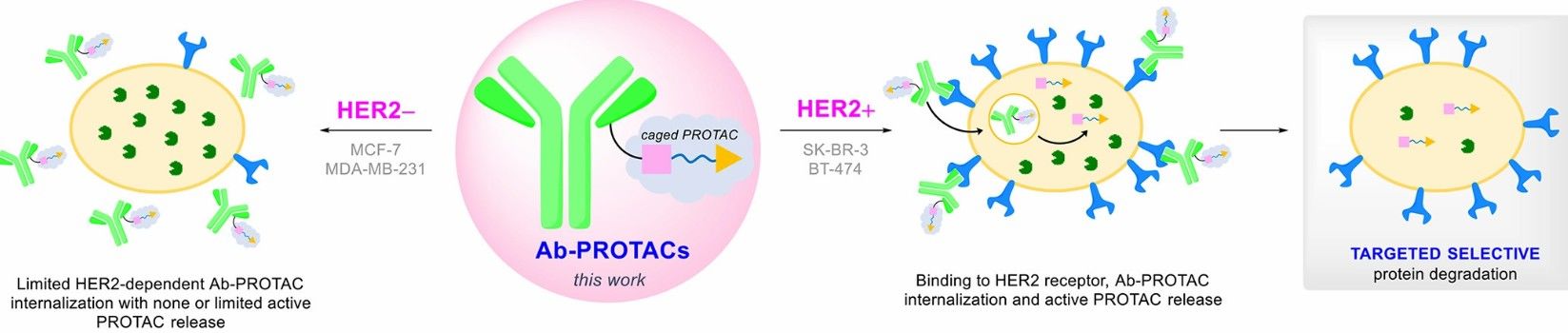 Fig. 1 mode of action of an antibody-PROTAC conjugate (Maneiro, 2020)
Fig. 1 mode of action of an antibody-PROTAC conjugate (Maneiro, 2020)
DAC Design
PROTAC in DAC contains target ligands that tend to exhibit more cancer-specific bioactivity than the broad cytotoxicity of ADC payloads. Therefore, the antigen selected for DAC must not only satisfy ADC internalization, but should also be highly expressed on tumors, tissues, or other cells sensitive to the biological pathways targeted by the PROTAC. In addition, since PROTACs are typically less toxic than ADC payloads, DACs may be required to have a higher drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR). If DACs are designed to be combined by cleavable linkers, the linkers attached to the PROTACs after antibodies catabolism in the lysosome should not interfere with their biological properties, and the PROTAC of the DAC in the lysosomal environment should have good stability as well as the ability to effectively escape the lysosomal compartment.
PROTAC-Antibody Conjugation
Since many PROTACs do not contain chemical groups that can be used for covalent attachment, such as amino groups, hydroxyl groups, the necessary chemical groups need to be purposefully incorporated into the PROTAC structure to achieve PROTAC-antibody conjugation. In the design of DACs, careful consideration needs to be given to appropriate linkers and conjugation methods, such as cleavable linkers (e.g. disulfide linker); non-cleavable linkers (e.g. maleimidocaproyl); and click chemistry reagents (e.g. strain alkyne-azide). When PROTACs are linked to antibodies, these linkers should facilitate the improvement of pharmacokinetic of DACs.
Application
Although the DACs are are still in the research stage, many DAC molecular entities have been successfully prepared using various PROTAC payloads and have shown promising in vitro and in vivo biological activity. For example, a DAC that attaches a BET PROTAC degrader (GNE-987) to an anti-CLL1 antibody showed strong antigen-dependent efficacy in xenograft tumor models; a trastuzumab-PROTAC conjugate selectively targeted BRD4 for degradation only in HER2 positive breast cancer cell lines, while sparing HER2 negative cells. Studies have shown that DACs can deliver PROTAC payloads potential to specific tumors or cells of interest. These promising preliminary results will provide a good foundation for future DAC development and applications.
References
- Pillow, T. H., et al., Antibody Conjugation of a Chimeric BET Degrader Enables in vivo Activity, ChemMedChem, 2020, 15, 17-25.
- Maneiro, M., et al., Antibody-PROTAC Conjugates Enable HER2-Dependent Targeted Protein Degradation of BRD4, ACS Chem. Biol., 2020, 15, 6, 1306-1312.
* PROTAC® is a registered trademark of Arvinas Operations, Inc., and is used under license.

 Fig. 1 mode of action of an antibody-PROTAC conjugate (Maneiro, 2020)
Fig. 1 mode of action of an antibody-PROTAC conjugate (Maneiro, 2020)