The BET proteins play a crucial role in regulating gene expression as epigenetic regulators and are involved in cancer pathogenesis. PROTAC targeted degradation of BET proteins has recently attracted increasing interest in the field of cancer therapy. PROTAC technology offers many potential advantages, such as good ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination) properties, overcoming target protein mutation-directed resistance, target various proteins including undruggable proteins. BOC Sciences is a leading CRO focused on the development of targeted protein degraders, and we have established comprehensive PROTACs development platform. We provide customized PROTAC development services based on the customer's PRTAC development needs for a particular target.
Introduction
The bromodomain and extra-terminal structural domain (BET) proteins family has two tandem bromodomains and one extra-terminal structural domain, including members BRD2, BRD3, BRD4 and BRDT. BET proteins play a key role in regulating gene transcription during cell proliferation and differentiation through epigenetic interactions between bromodomains and acetylated histones. In addition, BET proteins are involved in tumorigenesis, as well as mediating viral infection in host cells. Blocking the BET bromodomain with PROTAC protein degraders selectively inhibits the transcriptional, and these PROTACs are expected to be potential therapeutic agents for a variety of cancers.
PROTAC (proteolysis-targeting chimera) is a heterobifunctional small molecule compound capable of drawing target protein and intracellular E3 ligases into close proximity, resulting in a target protein-PROTAC-E3 ligase ternary complex that subsequently mediates polyubiquitination of the target protein and finally degrades the target protein specifically using the proteasome in the organism. Due to their unique chemical and biological properties, PROTACs have unique advantages in cancer therapy, such as targeting undruggable proteins and overcoming traditional drug resistance.
Design of BET-PROTAC Degrader
- A PROTAC degrader needs to contain a ligand that binds to the protein of interest (POI). A number of BET inhibitors have been reported that provide ample options for the development of BET-PROTAC. Small molecule inhibitors of BET proteins, such as (+)-JQ1, have been used to design pan-BET degraders (e.g. dBET1 , ARV-825) and selective BRD4 degraders (e.g. MZ1, dBET23).
- The choice of E3 ligase ligands is another important factor for PROTAC design. Several BET-PROTACs incorporating different E3 ligases have been shown to be effective, including VHL-, CRBN-, IAP-, and MDM2-based PROTACs. For example, MZ1, a VHL-based PROTAC, shows potent protein degradation activity. In addition, MZ1 was involved in the X-ray structure determination of the first PROTAC ternary complex BRD4-MZ1-VHL.
- Other key considerations for PROTAC design include the location of the linkage on the inhibitor and the chemical composition and length of the linker. The crystal structure can guide the choice of molecular attachment sites to avoid steric hindrance between the linker and the POI. The length of the linker can control the proximity to the POI and influence the efficiency of ubiquitination.
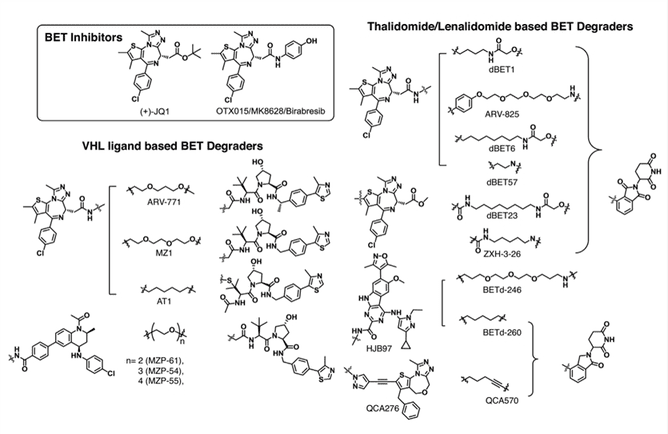 Fig 1. BET-PROTAC degraders (Yang, 2019)
Fig 1. BET-PROTAC degraders (Yang, 2019)
Our Advantages
- Customized PROTAC development based on BET proteins
- One-stop service for PROTAC targeting BET proteins degradation
- Short turn-around time and competitive price
- Data analysis, detailed report with results and discussion
- Multiple forms of PROTAC evaluation in vitro and in vivo
- High-throughput biochemical and cellular analysis, real-time kinetic analysis
- Biophysical assays for affinity characterization
Project Workflow
References:
- Taniguchi, Y., The Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Family: Functional Anatomy of BET Paralogous Proteins, Int J Mol Sci., 2016, 17(11): 1849.
- Yang, C., et al., Small-molecule PROTAC degraders of the Bromodomain and Extra Terminal (BET) proteins-A review, Drug Discovery Today: Technologies.

 Fig 1. BET-PROTAC degraders (Yang, 2019)
Fig 1. BET-PROTAC degraders (Yang, 2019)
