The landscape of drug targets has changed significantly over the past decade. While traditional targets are still the main direction, the trend is now slowly shifting from traditional drug targets to more challenging undruggable targets. These targets typically include proteins with no enzymatic function, which account for about 80% of the body's proteins. The hot proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) technology has shown great potential in overcoming drug resistance and targeting undruggable targets.
BOC Sciences is a contract research service provider. In recent years, BOC Sciences has strongly developed the PROTAC® protein degradation technology platform. Depending on the different requirements of our customers, BOC Sciences can design, synthesize and optimize PROTAC molecules and perform biological evaluations.
Introduction
PROTAC is a heterobifunctional small molecule compound that specifically degrades target proteins using the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in living organisms. Most small molecule inhibitors and antibodies act by occupancy-driven effect, i.e., by binding to the active site of the target protein and competing with endogenous substrates to inhibit the function of the protein. The mechanism of action of PROTAC differs from that of conventional drugs. PROTAC acts as a "catalyst", mediating the proximity of the target protein and the E3 ligase at low doses and in multiple cycles.
PROTAC is "event-driven" in that it mediates the degradation of the target protein, rather than affecting the function of the target. PROTAC may induce degradation of proteins without active sites, such as scaffold proteins, as long as they have a moderately effective target binding capacity, which greatly increases the range of targets.
About PROTAC Targets
Choosing the right target for degradation is critical, as drug development avoids affecting cell viability in normal tissues. One of PROTAC's development strategies is to select ligases that are low or nonexpressed in normal tissues, while being highly expressed in tumor cell types. The biological functions of the complete target include apoptosis, cell cycle regulation or division, transcription, cell signaling, or metabolism. The most common targets of PROTAC currently in preclinical development include the androgen receptor (AR), BRD4, EGFR and ALK.
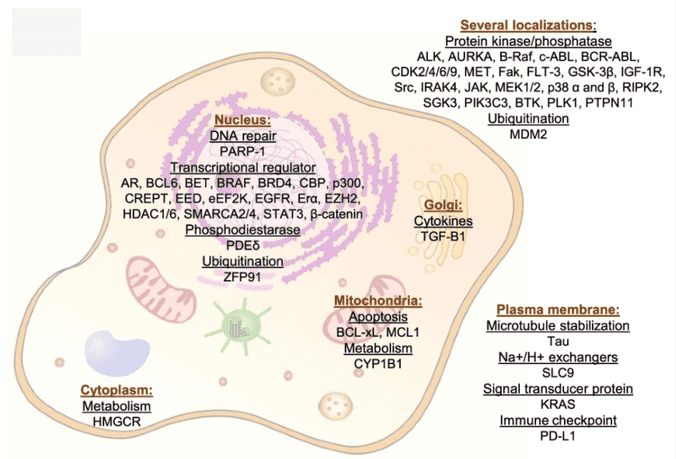 Fig 1. The targets and the functions they are involved in (Nieto-Jiménez, 2022)
Fig 1. The targets and the functions they are involved in (Nieto-Jiménez, 2022)
According to incomplete statistics, more than 100 proteins have been successfully degraded, including:
- Kinase classes, such as RIPK2, BCR-ABL, EGFR, HER2, c-Met, TBK1, CDK2/4/6/9, ALK, Akt, CK2, ERK1/2, FLT3, PI3K, BTK, Fak.
- Nuclear receptors, such as AR, ER.
- BET proteins, such as BRD2/4/6/9.
- Other proteins, such as MetAp-2, Bcl-xL, Sirt2, HDAC6, Pirin, SMAD3, ARNT, PCAF/GCN5, Tau, FRS2, etc.
These include undruggable targets such as RAS proteins that regulate signal transduction, transcription factor regulatory protein pirin, and epigenetically related protein PCAF/GCN5.
Our Services
As a leading CRO in the pharmaceutical field, BOC Sciences is dedicated to the design, screening, discovery and synthesis of effective PROTACs, assisting our customers in expanding the range of targets for targeted protein degraders and developing new PROTAC molecules. Our comprehensive PROTAC platform gives us the ability to perform the development of PROTAC molecules targeting various disease-associated proteins, including:
Our Advantages
- Customized drug development services based on customer-selected targets
- PROTAC development for different drug targets
- Quality one-stop service
- Experienced scientific team
- Data analysis, detailed results reporting and discussion
- Short turn-around time and competitive price
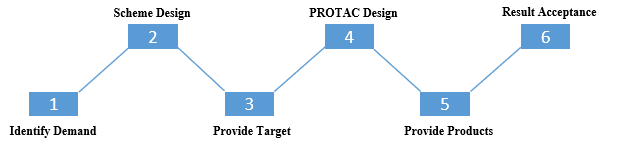
Project Workflow
References:
- Cromm, P. M., and Crews, C. M., Targeted Protein Degradation: from Chemical Biology to Drug Discovery, Cell Chem. Biol., 2017, 24, 1181-1190.
- Nieto-Jiménez, C., et al. Clinical considerations for the design of PROTACs in cancer, Molecular Cancer, 2022, 21, 67.

 Fig 1. The targets and the functions they are involved in (Nieto-Jiménez, 2022)
Fig 1. The targets and the functions they are involved in (Nieto-Jiménez, 2022)
