The development of lysosomal pathway-based degradation technologies provides new approaches to targeted protein degradation (TPD) and expands the toolbox for drug discovery. AUTAC is one of the new TPD technologies that have emerged in recent years, which works by exploiting the mechanism of cellular autophagy. BOC Sciences is a leading provider of contract research services in the field of targeted protein degradation. With our expertise and team of experienced scientists, we offer AUTAC degradation technology development services.
Introduction
Autophagy-targeting chimera (AUTAC) are the first degradation agents that use the autophagic mechanism. AUTAC is a heterobifunctional molecule with a targeting ligand and a label that recruits the autophagic system. A typical AUTAC consists of a small unit that binds to the substrate and a guanine derivative (degradation tag) connected by a flexible linker. AUTAC is able to penetrate cell membranes and degrade fragmented mitochondria as well as proteins. The concept of AUTAC was first proposed by Arimoto's group in 2019. It is reported that AUTAC can accelerate the removal of dysfunctional fragmented mitochondria and the biogenesis of functional mitochondria in patient-derived fibroblasts, acting as a protector for cells with acute mitochondrial damage.
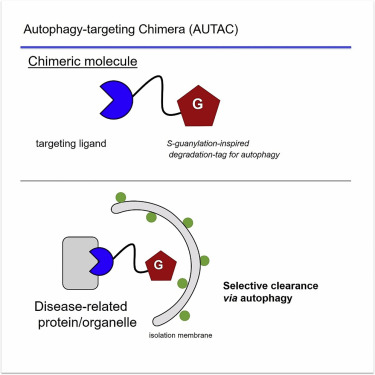 Fig 1. AUTAC degradation technology (Takahashi, 2019)
Fig 1. AUTAC degradation technology (Takahashi, 2019)
Autophagy is a multi-step degradation process that starts with the formation of phagophore. Subsequently, microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) transforms from the soluble form (LC3-Ⅰ) to the lipolytic form (LC3-Ⅱ) and binds to the phagophore to form autophagosome. AUTAC can induce position K63 polyubiquitination of protein of interest by mimicking S-guanylation modification through degradation tags, and recruit autophagosomes. The autophagosome recognizes and captures polyubiquitinated substrate through the surface receptor LC3, which in turn undergoes lysosomal pathway protein degradation.
AUTAC is capable of targeting intracellular proteins or organells. AUTACs have been successfully used to degrade a variety of disease-related target proteins, including methionine aminopeptidase 2 (MetAP2), FK506-binding protein (FKBP12), and BET family proteins. Although the specific degradation mechanism of AUTAC remains unclear, such as how polyubiquitinated degradation tags function, it provides researchers with new ideas on the degradation of target proteins, further expanding the range of target proteins. Therefore, there is a need to further develop the potential of AUTAC, such as exploring whether AUTAC can degrade protein aggregates.
Our Services for AUTAC Technology Development
- Design and optimization of AUTAC molecules.
- Screening, design, synthesis and optimization of POI-binding ligands based on different targets.
- Screening of compounds with high affinity for target proteins from compound databases by virtual screening technique.
- Chemical modifications to improve the properties of drug molecules.
- Chemical and biochemical analysis services covering every stage of preclinical drug development.
Our Advantages
- Dedicated to developing innovative AUTAC degradation technology
- Quality one-stop service
- Experienced experts team and extensive expertise
- Data analysis, detailed report with results and discussion
- Highly reliable and reproducible result
- Short turn-around time and competitive price
Project Workflow
References
- Takahashi, D., AUTACs: Cargo-Specific Degraders Using Selective Autophagy, Mol. Cell, 2019, 76, 797-810.e10.
- Takahashi, D., and Arimoto, H., Targeting selective autophagy by AUTAC degraders, Autophagy, 2020; 16(4): 765-766.

 Fig 1. AUTAC degradation technology (Takahashi, 2019)
Fig 1. AUTAC degradation technology (Takahashi, 2019)
