As a leading service provider in the field of drug discovery and research, BOC Sciences has extensive experience in targeted protein degradation therapies and the commercial development of PROTAC molecules. We are committed to providing one-stop PROTAC® based molecular drug discovery services, which has become a promising strategy for disease treatment. With a comprehensive and advanced platform, we provide PROTAC design services to help our clients develop new drug molecules to achieve their therapeutic disease goals.
Introduction
Proteolysis-targeting chimerics (PROTACs) are attracting more attention today as a potential treatment for cancer and other diseases. PROTACs consist of ligands, E3 ligase recruitment elements and junctions of target proteins. PROTACs can hijack the intrinsic intracellular ubiquitin proteasome system to degrade different target proteins.
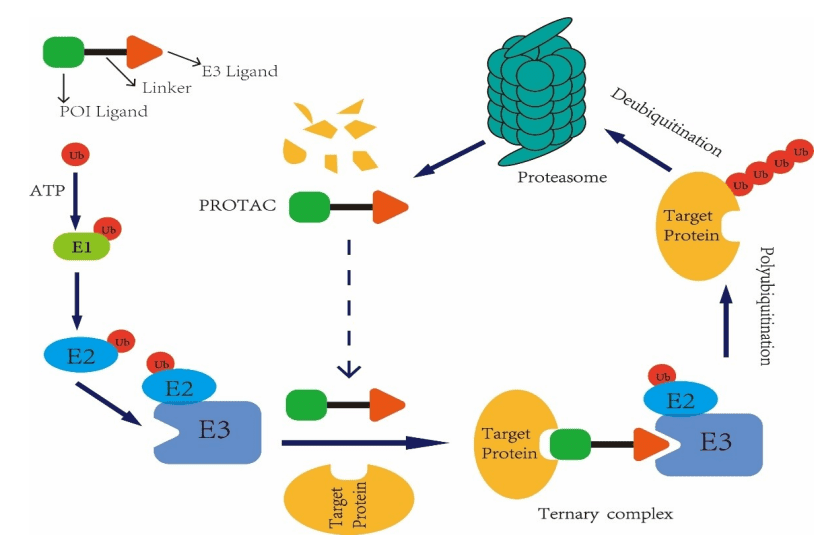 Fig 1. Acting mechanism of PROTAC molecules in vivo (Li, 2020)
Fig 1. Acting mechanism of PROTAC molecules in vivo (Li, 2020)
Cancer progression depends on the overexpression of proteins in many signaling pathways. The limitation of small molecule inhibitors for cancer treatment is that they act by binding to a structural domain of a protein, resulting in a very limited number of druggable targets. Given that PROTACs act by degrading rather than inhibiting the targets, they have the potential to become first-in-class drugs. Furthermore, PROTACs hold the promise of reaching the goal of exploiting undruggable targets.
Although the vast majority of newly developed PROTACs and molecular glue compounds currently in clinical trials target various types of cancer, however, the scope of PRTOACs goes further than oncology due to their potential to degrade any chosen target. Currently, PROTACs targeting disease-related proteins have been developed for the treatment of different diseases including cancer, inflammatory and immune diseases, viral infections, neurological diseases, etc.
PROTACs for Various Disease
| PROTAC Therapeutic Areas | Related PROTAC Products |
|---|
- PROTACs for Cervical Cancer
- PROTACs for Prostate Cancer
- PROTACs for Breast Cancer
- PROTACs for Lung Cancer
- PROTACs for Liver Cancer
- PROTACs for Lymphoma
- PROTACs for Leukemia
- PROTACs for Neuroblastoma (NB)
- PROTACs for Myeloma
- Autoimmune diseases
- Autoinflammatory diseases
- Cardiovascular disease
- Alzheimer's disease
- Huntington disease (HD)
- HCV infection
| | CAS 1949837-12-0 | Inquiry |
| CAS 1818885-28-7 | Inquiry |
| CAS 1799711-21-9 | Inquiry |
| CAS 2230077-10-6 | Inquiry |
| CAS 2349356-09-6 | Inquiry |
| CAS 1797406-69-9 | Inquiry |
| CAS 2064292-12-0 | Inquiry |
| CAS 2320561-35-9 | Inquiry |
| CAS 2230077-10-6 | Inquiry |
| CAS 2229036-62-6 | Inquiry |
| CAS 2231744-29-7 | Inquiry |
Although small molecule modulators targeting tumor cells are widely used, they still have some drawbacks such as drug resistance, toxicity and poor selectivity. PROTAC holds promise as a new therapeutic strategy to overcome the drawbacks of these drugs.
- PROTACs in neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are caused by the loss of neurons or their myelin sheaths. β-amyloid (Aβ) cascade and pathogenic tau protein are more like to be the target. Several cases of peptide-based PROTAC and small molecule-based PROTAC have been reported to degrade tau proteins, with important implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
- PROTACs in immune system diseases
Autoimmune diseases are those in which the body's immune response to self-antigens leads to damage of its own tissues and even to organ failure and death. For example, IRAK4, a key signal transducer and kinase downstream of the Toll signaling pathway, is involved in mediating various inflammatory responses. PROTAC molecules have been developed to target IRAK4 for degradation to achieve anti-inflammatory and immune modulating functions.
- PROTACs in virus infection
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the leading cause of acute and chronic hepatitis B. X-protein, a transactivator in HBV, plays an important role in the pathogenesis of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several peptide-based PROTAC molecules targeting X-proteins have been reported, which deserve to be investigated in preclinical studies for their ability to treat HBV infection and/or HCC.
Our Services
Our Advantages
- One-stop services of PROTAC design for disease treatment
- Well-established PROTAC platform
- Wide range of available small molecule ligands
- Expertise and experienced scientific team
- Data analysis, detailed results reporting and discussion
- Highly reliable and reproducible results
- Cost-effective and high-quality products
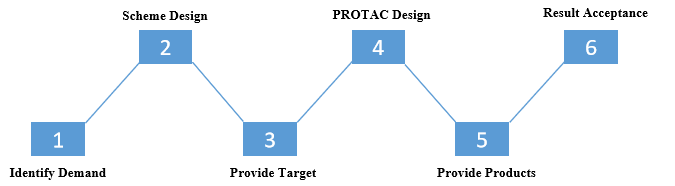
Project Workflow
References:
- Zhou, X., Dong, R., Zhang, J., Zheng, X., Sun, L., PROTAC: A promising technology for cancer treatment, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2020, 203, 112539.
- Li, J., and Liu, J., PROTAC: A Novel Technology for Drug Development, ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5, 13232-13247.

 Fig 1. Acting mechanism of PROTAC molecules in vivo (Li, 2020)
Fig 1. Acting mechanism of PROTAC molecules in vivo (Li, 2020)
