Lysosomal-Based Degradation Technology Development
We provide a variety of targeted degradation strategy development services based on the lysosomal pathway, covering multiple degradation needs such as transmembrane proteins, extracellular proteins, and antibody endocytosis targets, which are widely used in basic research, drug target verification, protein function research, and new drug development. We focus on lysosomal-based targeted degradation technology to help basic research and drug development. Services range from technical consultation, construction design to in vitro and in vivo functional verification to meet customers' personalized scientific research and transformation needs.
Request a Consultation Explore ServicesWhat is Lysosome-Based Targeted Protein Degradation?
Lysosomes play a vital role in the degradation and recycling of extracellular material and in maintaining cell homeostasis. Lysosomes function in two ways, endocytosis for extracellular material and autophagy for intracellular material. Lysosomes contain various hydrolytic enzymes which can break down proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, lipids, etc.
Lysosome-based targeted protein degradation is an emerging therapeutic and research strategy that harnesses the cell's natural lysosomal pathway to selectively degrade unwanted or disease-associated proteins-particularly those located on the cell surface or in the extracellular space. Unlike proteasome-based systems such as PROTACs, which primarily target intracellular proteins, lysosome-mediated approaches enable the degradation of membrane-bound and secreted proteins, dramatically expanding the scope of druggable targets.
At its core, this strategy involves tagging the target protein with a molecule (such as an antibody or ligand) that can recruit cellular receptors capable of initiating endocytosis. Once internalized, the tagged protein is trafficked to lysosomes, which are acidic organelles equipped with hydrolases that break down biological macromolecules.
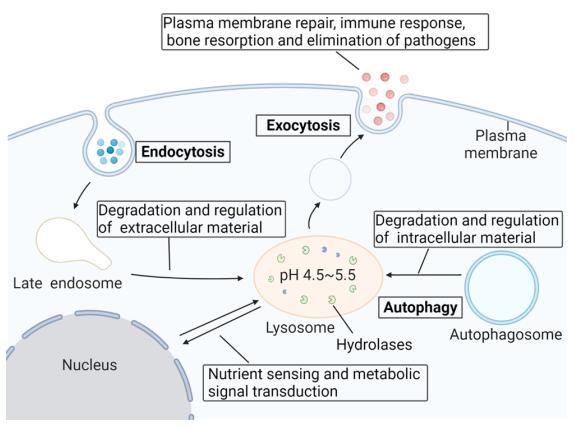 Fig 1. The lysosomal degradation pathway (Pei, 2021)
Fig 1. The lysosomal degradation pathway (Pei, 2021)
Key Features of Lysosomal Protein Degradation
Targets extracellular and transmembrane proteins that are inaccessible to proteasomal degradation.
Utilizes endogenous cellular pathways such as receptor-mediated endocytosis (e.g., CI-M6PR, ASGPR) or autophagy.
Compatible with various formats including antibodies, small molecules, peptides, and chimeric degraders (e.g., LYTACs, AUTACs).
Enables selective and potent degradation without requiring genetic manipulation.
Services
Our Services for Lysosomal-Based Technology Development
Target Assessment and Degradability Prediction
Objective: Support clients in evaluating whether target proteins are suitable for lysosome-based degradation pathways.
- Subcellular localization analysis (membrane-bound, intracellular, or secreted proteins)
- Expression profiling and intracellular trafficking prediction (via public databases or experimental data)
- Compatibility assessment with lysosomal degradation pathways
- Recommendation of suitable degradation platforms (e.g., LYTAC vs. ATTEC)
Objective: Develop customized LYTAC molecules using antibodies or ligands to degrade membrane proteins.
- Antibody selection or sourcing (commercial or custom-made)
- Design and synthesis of M6Pn or ASGPR ligands
- Antibody-ligand conjugation strategies (chemical conjugation or bispecific formats)
- Purity and functional validation of synthesized LYTACs
ATTEC/AUTAC Small Molecule Design and Screening
Objective: Design and identify small molecules capable of recruiting target proteins to the lysosomal degradation pathway.
- LC3-binding module design for ATTEC compounds
- Ubiquitination-activating module design for AUTAC molecules
- Fragment-based screening for bifunctional degraders
- In vitro degradation efficacy assays
AbTAC Bispecific Antibody Construction
Objective: Construct bispecific antibodies that link target proteins to lysosomal degradation pathways.
- Antibody format design (scFv, diabody, etc.)
- Affinity testing and bispecific antibody engineering
- Bispecific antibody expression and purification
- Functional assays in cell-based systems
Receptor Targeting and Endocytosis System Design
Objective: Identify and leverage specific endocytic receptors (e.g., ASGPR, CI-M6PR, TfR) to enhance intracellular delivery efficiency.
- Target tissue/cell receptor profiling (literature and experimental validation)
- Ligand screening and receptor-binding verification
- Design of targeted delivery strategies
In Vitro Functional Validation Services
Objective: Verify degradation molecule activity and underlying mechanisms through cellular assays.
- Western blot/ELISA to assess target protein degradation efficiency
- Endocytosis and lysosome colocalization (LysoTracker + confocal microscopy)
- Immunofluorescence co-staining and quantitative analysis
- Degradation kinetics profiling (cycloheximide chase assay)
- Reporter system development (GFP-tag, luciferase)
High-Throughput Screening Platform (HTS)
Objective: Provide large-scale primary screening and validation for small molecule degraders.
- Screening libraries: LC3-binding ligands and target-specific ligands
- Custom-built degradation activity assay platforms (fluorescence reporters, antibody-based detection)
- Automated data analysis and hit validation
PK/PD and Preliminary Efficacy Evaluation
Objective: Generate supportive data for preclinical and clinical development.
- Stability analysis of LYTAC/ATTEC molecules in serum
- Tissue distribution and target-specific degradation assessment in animals
- PK/PD modeling and simulation support
- Early-stage safety evaluation (immune activation, lysosome saturation)
Custom Collaborative Projects and Co-Development
Objective: Provide end-to-end project solutions from target discovery to IND filing.
- Tailored solutions: from target validation to molecule synthesis and mechanism of action confirmation
- Support for co-patenting, co-publication, and technology licensing
- Flexible collaboration models: milestone-based services, success-fee contracts, joint development partnerships
Advantages
Our Service Advantages in Lysosomal Protein Degradation
01.Multi-Platform Expertise
We offer end-to-end technical capabilities across all major lysosome-based degradation platforms, including LYTAC, AUTAC, ATTEC, and AbTAC. Our team is experienced in choosing and optimizing the most appropriate modality based on target location, structure, and cellular context.
02.Custom Molecular Design
Whether it's bifunctional small molecules or antibody-ligand conjugates, we provide fully customized design services. This includes ligand sourcing, linker chemistry, conjugation strategy, and receptor targeting for efficient internalization and lysosomal delivery.
03.Receptor Targeting Strategies
Our team has deep expertise in designing degraders that leverage various lysosomal targeting receptors such as CI-M6PR, ASGPR, and transferrin receptor. We tailor receptor-ligand systems based on your target cell type to ensure optimal uptake and degradation efficiency.
04.Integrated In Vitro Validation
We provide comprehensive cell-based validation services, including degradation kinetics (e.g., CHX chase), lysosomal colocalization imaging, and downstream functional assays. You receive robust data demonstrating proof of mechanism and efficacy.
05.Flexible Collaboration Models
From standalone design or synthesis to complete hit-to-lead or IND-enabling studies, we support flexible collaboration models. We can serve as a strategic CRO partner or scientific co-developer, depending on your project needs and timeline.
06.Fast Turnaround and Expert Support
Our streamlined workflows and deep scientific bench allow for fast, responsive project execution. Every project is guided by PhD-level scientists with expertise in chemical biology, immunology, and targeted degradation.
Workflow
End-to-End Development of Lysosome-Based Targeted Protein Degraders
We offer a fully integrated, stepwise workflow tailored to your project needs-whether you are developing a LYTAC, AUTAC, ATTEC, AbTAC, or other lysosome-targeting modality.
Target Assessment
Protein profiling
Degradation fit
Strategy suggestion
Feasibility report
Molecule Design
Degrader types
Ligand synthesis
Antibody linkage
In Vitro
Internalization
Trafficking
Degradation test
Mechanism probe
Mechanism Validation
Pathway readout
Kinetics
Dependency check
In Vivo (Optional)
Animal models
PK/Distribution
Degradation assay
Safety profile
Data Transfer
Report delivery
IP support
Tech transfer
Application
Application Areas of Lysosome-Based Targeted Protein Degradation
Transmembrane Protein Degradation
Targeting EGFR, PD-L1, LAMP2, and Other Cell Surface Proteins
Lysosome-based technologies like LYTAC and AbTAC enable selective degradation of membrane proteins such as EGFR, PD-L1, and LAMP2 for applications in cancer and metabolic diseases.
Clearance of Aggregated Proteins
Targeting Misfolded Proteins Like α-Synuclein, TDP-43, and Tau
ATTEC and AUTAC platforms promote the removal of misfolded proteins like α-synuclein, TDP-43, and Tau in neurodegenerative disease research.
Mitochondrial Quality Control
Regulating Mitophagy via Parkin, PINK1, and LC3
Lysosome-driven strategies regulate mitophagy through Parkin, PINK1, and LC3 to eliminate damaged mitochondria in metabolic and cardiovascular disorders.
ADC and Targeted Delivery Systems
Designing Lysosome-Targeted Conjugates and Receptor-Mediated Uptake Pathways
LYTAC and AbTAC enable targeted drug delivery via lysosome-targeting conjugates and receptor-mediated uptake mechanisms like ASGPR and CI-M6PR.
Innovative Drug Screening and Target Validation
Discovering Degradable Targets and Assessing Compound Efficacy
Lysosomal pathways support high-throughput drug screening and validation by identifying degradable targets and assessing compound efficacy.
Discover Products for Your Research

- Precise Screening
- Cellular Phenotypic Assays
- Targeted Degradation Profiling

- Pharmacodynamics Monitoring
- Tissue-Specific Degradation
- Long-Term Toxicity Studies

- Ligase Engineering
- Ligase-Targeted Synergy
- Modular Ligase Systems

- High-Yield Expression
- Protein Engineering
- Biochemical Characterization

- Lysosomal Targeting
- Novel Degradation Pathways
- Selective Autophagy Activation

- Enhanced Ubiquitination
- Improved Targeting Effect
- Degradation Rate Modulation

- Personalized Drug Design
- Multitargeted Drug Design
- Disease-Driven Optimization

- Targeted Custom Design
- High Selectivity and Efficiency
- Enhanced Affinity
Further Reading on Related Topics
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What types of proteins can be targeted using lysosome-based degradation technologies?
Lysosome-based approaches, such as LYTAC and AbTAC, are ideal for targeting extracellular and membrane-bound proteins. Newer modalities like ATTEC and AUTAC also enable intracellular protein clearance by leveraging autophagy pathways.
2. How do I choose between LYTAC, AUTAC, ATTEC, and AbTAC?
The choice depends on your target protein's location, structure, and biological context. For example, LYTACs are best for membrane proteins with accessible extracellular domains, while AUTAC/ATTEC are better suited for intracellular targets. Our scientific team will help evaluate your target and recommend the most suitable platform.
3. Do you offer end-to-end service, or can I outsource specific parts (e.g., molecule synthesis only)?
Yes, we offer flexible collaboration. You can engage us for complete end-to-end services (from design to validation), or for specific modules such as ligand screening, antibody conjugation, or in vitro degradation assays.
4. Is this technology suitable for therapeutic development?
Yes. Lysosome-targeted degradation platforms are being actively explored for drug development, particularly in oncology, immunology, and neurodegenerative diseases. Our workflow includes translational support and preclinical validation options to bridge discovery and therapeutic development.


 Fig 1. The lysosomal degradation pathway (Pei, 2021)
Fig 1. The lysosomal degradation pathway (Pei, 2021)

