As a CRO that has been deeply involved in the field of PROTAC for over a decade, BOC Sciences provides PROTAC design services for various targets. The PROTACs are considered as a good therapeutic strategy for targeting androgen receptor (AR) signaling in prostate cancer cells. With extensive expertise and comprehensive platform, we provide AR-targeting PROTACs design, synthesis, and evaluation services, in order to accelerate our clients' new drug development process.
Find out more with PROTAC Design for Target Proteins.
Introduction
Androgen receptor (AR) is a ligand-dependent nuclear transcription factor and member of the steroid hormone nuclear receptor family. Given its widespread expression in many cells and tissues, the AR has a diverse range of biological actions including important roles in the development and maintenance of the reproductive, musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, immune, neural and haemopoietic systems. AR signalling may also be involved in the development of tumours in the prostate, bladder, liver, kidney and lung.
The AR comprises three main functional domains: the N-terminal transcriptional regulation domain, the DNA binding domain (DBD) and the ligand binding domain. AR plays crucial roles in prostate cancer, especially castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). AR signaling suppression is a common strategy for treating prostate cancer. Androgen deprivation therapy can suppress most prostate cancers, but some high-risk prostate cancers gradually progress to CRPC, which can grow under castrated levels of androgen.
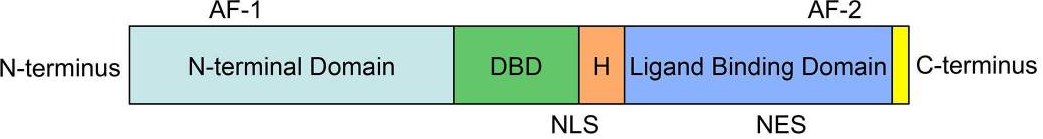
AR PROTAC
A typical PROTAC (Proteolysis targeting chimera) is a heterobifunctional molecule consist of a ligand, which binds to the target protein (in this case AR), and is tethered by a chemical linker to a second ligand, which binds to and recruits an E3 ligase system. PROTAC induces AR protein degradation through the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system. Using a potent AR antagonist, an E3 ligase ligand together with an appropriate linker needs to be carefully considered in the design of a highly potent and effective AR PROTAC degrader to form an efficient ternary degradation complex and achieve efficient degradation of AR.
Current PROTACs for AR
On the PROTACs against AR, study reported a hybrid molecule, ARCC-4, consisting of enzalutamide (an antiandrogen) linked to a VHL ligand via a linker. ARCC-4 induced the degradation of AR in not only all prostate cancer cell lines but also a breast cancer cell line. A small molecule-based PROTAC, ARV-771, using pan-BET inhibitors suppressed both AR protein level and AR signalling, shown the efficacy in cellular models of CRPC. The PROTAC ARV-110 targeting the AR is one of the rationally designed targeted protein degraders into first-in-human trials. Currently, several PROTACs are in early clinical development. They are disclosed to be ARV-110, ARV-766, and CC-94676, all of which target the nuclear receptor AR, as well as administered via the oral route.
SNIPERs for AR
Specific and nongenetic inhibitor of apoptosis protein [IAP]-dependent protein erasers (SNIPERs) that recruit IAP ubiquitin ligases to degrade target proteins. Through optimization of the SNIPER molecule at the AR ligand and IAP ligand and linker, the SNIPER(AR)s have been developed. Studies suggest that SNIPER(AR)s could be leads for an anticancer drug against prostate cancers that exhibit AR-dependent proliferation.
Our Services of AR PROTAC Development
- AR-binding ligands Library.
- AR PROTAC chemical synthesis. A PROTAC molecule is is covalently connected through a AR ligand, a linker and an E3 ligand.
- Binary binding affinity assay. PROTACs to AR and E3 ligase are determined by using surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
- PROTAC activity assay. The target protein AR levels are determined by Western blot.
Related Products
We also provide target proteins, learn more Nuclear Receptors.
Our Advantages
- One-stop services of AR-PROTAC design
- Design and selection of small molecule ligands
- Data analysis, detailed results reporting and discussion
- Expertise and experienced scientific team
- Cost-effective and high-quality products
References
- Davey, R. A., and Mathis, G., Androgen Receptor Structure, Function and Biology: From Bench to Bedside, Clin Biochem Rev., 2016, 37(1): 3-15.
- Zou, Y., Ma, D., Wang, Y., The PROTAC technology in drug development, Cell Biochem. Funct, 2019, 37, 21-30.


