As a leading CRO in the pharmaceutical industry, BOC Sciences provides customized PROTAC design services for various targets. The bifunctional PROTAC compounds are useful as modulators of targeted ubiquitination with respect to Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases 4 (IRAK4), which is degraded by these compounds. IRAK4 is an emerging target for PROTAC molecules against multiple diseases, including hematologic malignancies and autoimmune diseases. With extensive expertise and comprehensive platform, we provide PROTAC molecules design services to target IRAK4.
Introduction of IRAK4
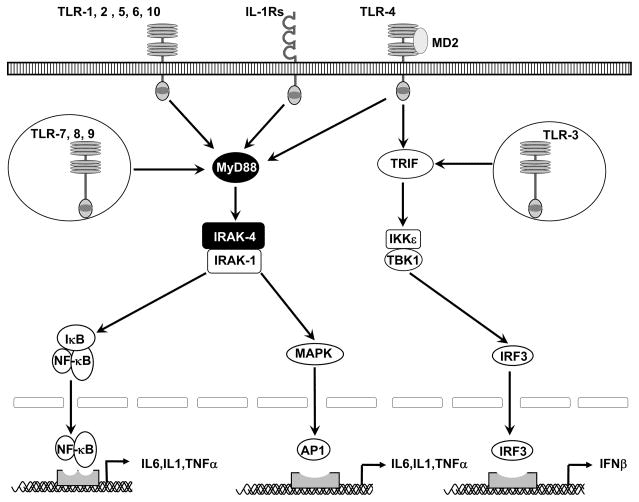
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) is a serine, threonine kinase that performs an important function of scaffolding and phosphorylation in toll-like receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling pathways. These receptors that recognizing foreign pathogens and inflammatory signals promotes IRAK4 binding to the adapter protein myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88) resulting in IRAK4 activation that in turn leads to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines via the NFκβ pathway. Additionally, IRAK-4 and IRAK-1 activate the signaling mitogen-activation protein kinases (MAPK) pathway that leads to activator protein 1 (AP-1)- induced gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
IRAK4 overactivation is linked with several autoimmune diseases. Activation of the IRAK4 pathway triggers an inflammatory chemokine and cytokine cascade that is important in innate immunity. Therefore, Inhibition or elimination of IRAK4 blocks pro-inflammatory cytokine production in humans and represents a promising therapeutic approach in autoimmune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, hidradenitis suppurativa. In addition, cell intrinsic and extrinsic perturbations to inflammatory signaling pathways are a hallmark of development and progression of hematologic malignancies. Thus IRAK4 is considered as a promising therapeutic target for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
IRAK4 PROTAC
Targeted protein degradation using the proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) technology has emerged as a novel therapeutic modality in drug discovery. IRAK4 PROTAC consists of three key structural components: a IRAK4 ligand, an E3 ubiquitin ligase recruiting ligand, and a linker connecting these two ligands. PROTACs mediate the degradation of selected target by hijacking the activity of E3 ubiquitin ligases for target ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by the proteasome system.
In addition to the kinase activity of IRAK4, studies have shown that the scaffolding function of IRAK4 plays an important role in the MYD88-IRAK4-NFκB signaling pathway. Several potent and selective inhibitors of IRAK4 have been reported in the literature. However, inhibiting IRAK4 kinase activity alone by these inhibitors may not be sufficient to produce a therapeutic effect due to the role of IRAK4 as both a scaffolding protein and an active kinase. Unlike conventional inhibitors that only inhibit IRAK4 kinase activity, PROTAC degraders of IRAK4 may eliminate both the kinase and scaffolding functions, providing a more potential approach to treat autoimmune, inflammatory, and oncological diseases.
Current PROTACs Targeting IRAK4
Study reported a small molecule PROTAC using the Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) E3 ligase ligand in 2019, achieving potent intracellular degradation of the kinase IRAK4, with a DC50 of 151 nM in PBMC cells. Yun Chen, et al. have reported a PROTAC molecule that potently degrades kinase IRAK4 in OCILY10 and TMD8 cells in 2020. The IRAK4 PROTAC shown a substantial advantage in inhibiting the growth of cell lines expressing the MYD88 L265P mutant compared with the IRAK4 inhibitor.
Currently, there are two IRAK4 PROTAC compounds in clinical development, KT-474 and KT-413. KT-474 is the first IRAK4 degrader, and first PROTAC outside of oncology, to enter clinical development. Compared to monoclonal antibodies targeting single cytokines, KT-474 is designed to block TLR/IL-1R-mediated inflammation more broadly and achieve superior pathway inhibition to IRAK4 inhibitors by abolishing both the kinase and scaffolding functions of IRAK4. KT-413 is being developed initially for the treatment of MYD88-mutant DLBCL, with the potential to expand into other IL-1R/NFkB malignancies. KT-413 is currently in preclinical development.
Our Services of IRAK4 PROTAC Development
- Using Cocrystal structure of small molecule with IRAK4 kinase domain to guide the design of IRAK4 PROTAC.
- Performing small molecule docking to predict the best position of IRAK4 to attach linkers.
- Screening and optimization of ligands of E3 ligase such as VHL, Cereblon (CRBN) , or the Inhibitor of Apoptosis (IAP).
- Synthesizing IRAK4 PROTAC by assembling a IRAK4 ligands, a linker and an E3 ligands to meet the individual requirements of customers.
- Assessing binding affinities of PROTACs to IRAK4 and E3 ligase, and efficacy of PROTAC for depletion of IRAK4 levels.
Our Advantages
- One-stop services of IRAK4-PROTAC design
- Design and selection of small molecule ligands
- Expertise and experienced scientific team
- Data analysis, detailed results reporting and discussion
- Cost-effective and high-quality products
Project Workflow
References
- Nunes, J., et al., Targeting IRAK4 for Degradation with PROTACs, ACS Med Chem Lett., 2019, 10(7): 1081-1085.
- Picard, C., et al., Clinical Features and Outcome of Patients With IRAK-4 and MyD88 Deficiency, Medicine (Baltimore)., 2010, 89(6): 403-425.



