BOC Sciences is a leading CRO in the pharmaceutical industry, and our one-stop PROTAC service covers every aspect of PROTAC research. A significant advancement of the PROTAC technology was the identification of small molecule-based E3 recruiting ligands. PROTAC degraders using VHL and other E3 ligases with known ligands have modular properties. We are able to provide E3 ligase VHL-based PROTAC development services. With comprehensive platform and expertise, we have focused on PROTAC development to better assist our clients' new drug research.
Introduction of VHL
The von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein is a part of the multiprotein complex, along with elongin B and C, cullin 2 and RING-Box protein (Rbx-1), which possesses an E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. VHL is a substrate recognition subunit of the biologically important Cullin RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. VHL folds into two domains, one of which is responsible for the binding of specific substrates. VHL is one of the most popular E3 ligases being recruited by bifunctional Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) to induce ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of a target protein. In addition, VHL is an important tumor suppressor of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), which can target hypoxia inducible factors α (the primary substrate is HIF-1α) for proteasomal degradation. Studies have shown VHL also has HIF-independent functions. Thus, there are many PROTACs that use VHL as the E3 ubiquitin ligase to degrade the target protein.
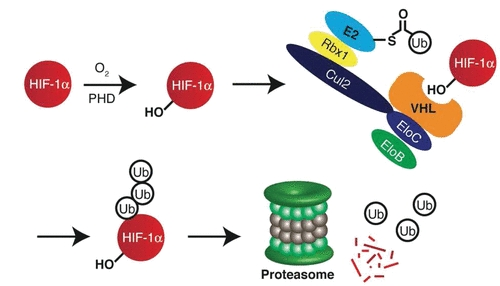 Fig 1. HIF-1α is recognized by VHL and degraded by the proteasome (Buckley, 2012)
Fig 1. HIF-1α is recognized by VHL and degraded by the proteasome (Buckley, 2012)
VHL-based PROTACs
E3 ubiquitin ligases are key players in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway because they catalyse ubiquitination of substrate proteins. VHL is extensively targeted with PROTAC compounds and has been successfully utilized for degrading more than 20 different proteins. VHL-based PROTAC is a heterobifunctional compound with three parts: a VHL-binding ligand, a target protein-binding ligand, and a linker for conjugating these two ligands.
Early VHL-based PROTACs utilized 5-7 amino acid long sequences derived from HIF-1α protein, due to the lack of small molecule VHL ligands. Peptidomimetic binding moieties with high VHL-binding affinity have been developed in 2012 and have since been widely used in PROTACs. The development of VHL ligands could requires the determination of derivatization without negatively affecting the affinity of the critical binding sites.
Current VHL PROTACs Development in Clinica Trials
Although VHL is one of the most popular E3 ligases, CRBN appears to be the preferred E3 ligase in the first wave of clinical trials with PROTAC degraders. A notable exception is a BCL-xL degrader known as DT2216 that uses VHL as the recruiting ligase, which is in phase I trials. Overexpression of anti-apoptotic proteins such as BCL-xL will promote the development and progression of cancer. DT2216 has shown strong inhibitory effects on all kinds of BCL-xL -dependent leukemia and cancer cells in vitro. Due to the poor expression of VHL in platelets, DT2216 has low toxicity to platelets because of the poor expression of VHL in platelets.
Our Services
- Developing VHL ligands with a solid binding affinity via the analysis of co-crystal structures and other methods.
- Identifying affinity of ligand candidates for E3 Ligase VHL.
- Affording the ability to tailor the ligase to the target protein by using an inhibitor of choice against the target protein and a ligase-recruiting molecule that are connected.
- Assaying the stability, cell permeability, solubility and tissue distribution of VHL-based PROTAC.
Related Products
Our Advantages
- Customized VHL-based PROTACs development
- Advanced technology and experienced scientific team
- Highly reliable and reproducible result
- Data analysis, detailed report with results and discussion
- Short turn-around time and competitive price
- One-stop PROTAC discovery services.
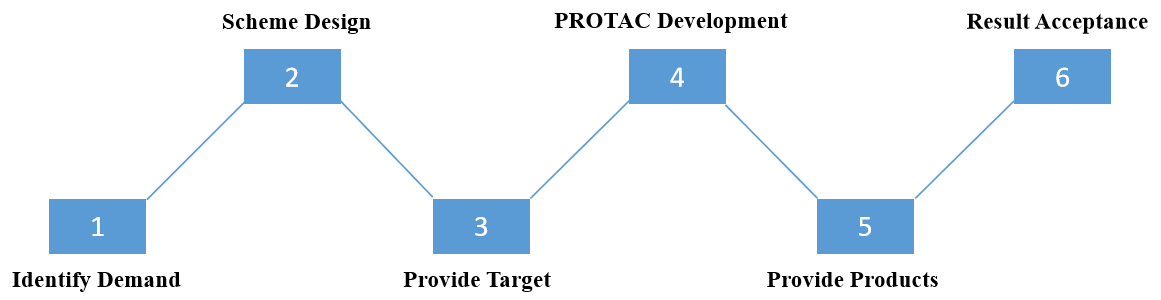
Project Workflow
References
- Khan, S., et al., A Selective BCL-XL PROTAC Degrader Achieves Safe and Potent Antitumor Activity. Nat. Med., 2019, 25, 1938-1947.
- Buckley, D. L., et al., Targeting the von Hippel–Lindau E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Using Small Molecules To Disrupt the VHL/HIF-1α Interaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10, 4465-4468.

 Fig 1. HIF-1α is recognized by VHL and degraded by the proteasome (Buckley, 2012)
Fig 1. HIF-1α is recognized by VHL and degraded by the proteasome (Buckley, 2012)






