ALK gene rearrangement, also known as the diamond mutation. ALK is mainly expressed in the nervous system, it is closely associated with the development of many tumors. ALK inhibitors are commonly used as a treatment, but it inevitably has the problem of drug resistance. PROTAC has been proposed as an alternative approach for the treatment of ALK-related diseases and to overcome drug resistance.
As a leading CRO, BOC Sciences is dedicated to construct protein targeted degradation platform. With our extensive expertise and integrated platform, we provide ALK-based PROTAC development services to help our clients with drug discovery.
Introduction of ALK
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily. ALK genes activate several intracellular signaling pathways that are involved in the regulation of cell growth, transformation and anti-apoptotic processes. ALK is highly conserved across species and is expressed in the adult brain, where it is thought to play an important role in the development and function of the nervous system. ALK is also expressed in the small intestine, testis, prostate and colon but not in normal lymphoid tissue, lung and other tissue. ALK was first identified in a subtype of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). In addition, multiple types of ALK gene rearrangements were identified in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT), neuroblastoma and lymphoma, respectively, thus demonstrating that ALK is a potent oncogenic driver gene. ALK fusions are important therapeutic targets in NSCLC. ALK fusion is the second major molecular subtype of NSCLC after EGFR mutations and has been developed as a classical tyrosine kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) target with multiple generations of inhibitors, including first-generation crizotinib, second-generation ceritinib, alectinib, and brigatinib, third-generation lorlatinib.
About ALK PROTACs
Although several ALK inhibitors have entered clinical trials, the emergence of drug resistance has limited their clinical use. To overcome resistance, ALK PROTACs may be an alternative strategy. Drug resistance mechanisms are usually associated with ALK mutations, and therefore targeted degradation of ALK could theoretically improve drug treatment efficacy. ALK PROTACs consist of three components, a ligand for binding ALK, an E3 ligase-binding ligand, and a linker connecting the two ligands. The ALK PROTAC is a chemical knockdown strategy that recruits a specific protein target to an E3 ubiquitin ligase, resulting in ALK ubiquitination and degradation. PROTACs in their ability to induce protein ubiquitination exhibit catalytic effects, which is a key advantage over small molecule inhibitors.
ALK PROTACs are designed with the strategy of connecting ALK inhibitors to E3 ligase ligands such as pomalidomide through linkers of different lengths and types. The most commonly used E3 ligase ligands include cereblon (CRBN) ligands and von-Hippel-Lindau (VHL) ligands. The CRBN ligands include thalidomide, lenalidomide, and VHL ligands include VH032 and its derivatives VH032-cyclopropane-F, VH-298, etc.
Progress of ALK PROTACs
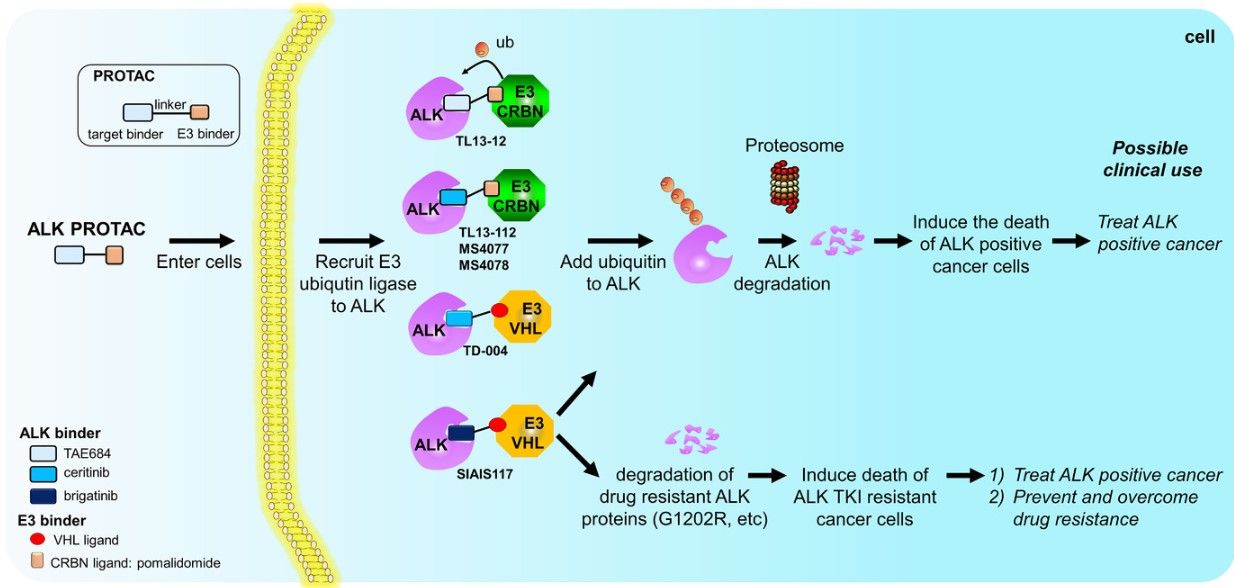 Fig. 1 Examples of ALK PROTACs (Song, 2021)
Fig. 1 Examples of ALK PROTACs (Song, 2021)
PROTAC targeting ALK fusion protein degradation has been reported. In 2018, PROTACs designed to target ALK, MS4077 and MS4078, TL13-112 and TL13-12, using ALK inhibitors and pomalidomide, have been reported. These ALK-based PROTACs significantly reduced the cellular levels of ALK fusion proteins in different cell lines and mediated the ubiquitination and degradation of NPM-ALK and EML4-ALK in vitro. In addition, TD-004, developed using VHL ligands, degraded NPM-ALK in ALCL cell lines, and EML4-ALK in NSCLC cell lines at a concentration of 300 nM. Another VHL-based PROTAC, SIAIS117, which uses brigatinib as an ALK ligand, was reported to degrade G1202R mutant ALK in vitro.
| Name | CAS | ALK ligand | E3 type | E3 ligand |
|---|
| MS4077 | 2230077-10-6 | Ceritinib | CRBN | Pomalidomide |
| MS4078 | 2229036-62-6 | Ceritinib | CRBN | Pomalidomide |
| TL13-112 | 2229037-19-6 | Ceritinib | CRBN | Pomalidomide |
| TL13-12 | 2229037-04-9 | TAE684 | CRBN | Pomalidomide |
| TD-004 | | Ceritinib | VHL | VHL ligand |
| SIAIS117 | 2353494-84-3 | Brigatinib | VHL | VHL ligand |
Our Services
- Development of small molecular ligands targeting ALK
- Linker selection and optimization
- Design and synthesis of ALK PROTACs
- Analysis of ALK-PROTAC-E3 ligase ternary complex
- ALK PROTACs activity assay
- Protein degradation assay
Related Products
Our Advantages
- Custom PROTAC development based on ALK target
- Comprehensive PROTAC platform and experienced scientific team
- Quality one-stop service
- Experienced experience in developing ALK ligands
- Short turn-around time and competitive price
- Highly reliable and reproducible result
Reference
- Song, X., et al. Two novel strategies to overcome the resistance to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor drugs: Macrocyclic inhibitors and proteolysis-targeting chimeras, MedComm, 2021, 2, 341-350.

 Fig. 1 Examples of ALK PROTACs (Song, 2021)
Fig. 1 Examples of ALK PROTACs (Song, 2021)